CPNB
Continuous Peripheral Nerve Block
Continuous Peripheral Nerve Block (CPNB);
when the anesthetic medication is delivered close proximity to a peripheral nerve that controls the organ that been treated by the surgery.
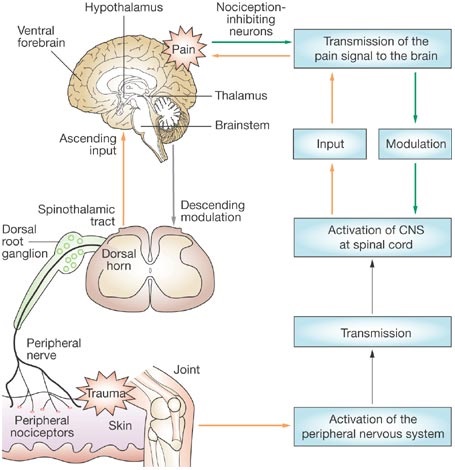
The pain being
anaesthetizing by continuously delivery of anesthetic medication near to the peripheral nerve.
Efficient nerve block is obtained once the medication is surrounding over the nerve cord at at-least 180° of its circumference along a segment of about 10 mm long and profound nerve block is obtained once the medication is fully (360°) surrounding the nerve cord at segment of about 10 mm long - a "shut off" the Peripheral nociceptors is obtained
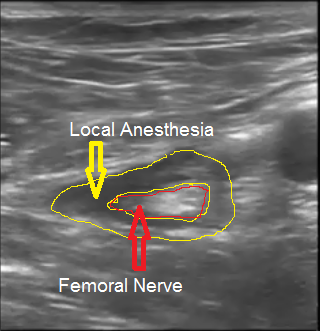
The femoral nerve is fully surrounded by the LA "pancake" like
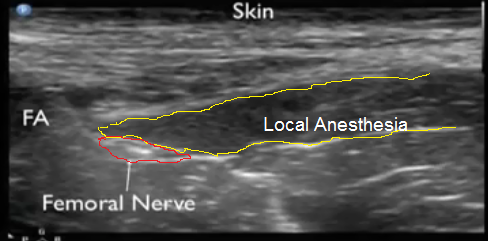
The LA covering about half of the circumference of the femoral nerve; efficient the pain blockage is achieve (but not profound blockage)
A. Most common Continuous Peripheral Nerve Block procedures
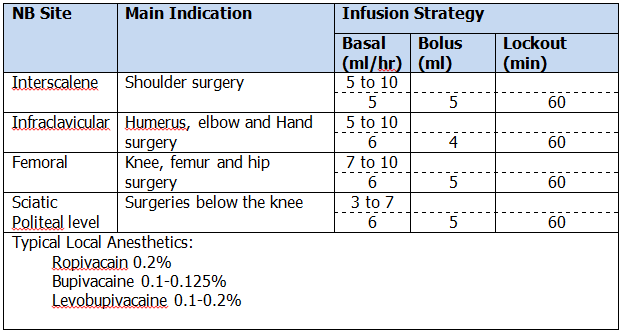
Important Note
The data and information concerning "Most common Continuous Peripheral Nerve Block procedures" is based on public domain publications and should serve as general indication only and not as instructions and/or recommendations!
This data isn't a scientific data!
It is strictly the responsibility of the physician to make the any decisions concerning the medication infusion therapy!
B. Factors Influencing on the Therapy Efficiency
1. General
> Position of the catheter
> Medication: type, concertation
2. Continuous Basal Flow
> Flow rate
3. Bolus
> Bolus volume
> Velocity rate
